With the aim of creating a sustainable society, vehicle fuel economy standards are becoming progressively tighter year by year in order to reduce carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions. It is forecast that the proportion of the total market accounted for by electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) will grow significantly by 2020. HEVs have been commercialized in a variety of forms. Hitachi Automotive Systems Americas, Inc. draws on its strengths in power electronics to supply inverters that suit diverse customer requirements.

(2 motors)
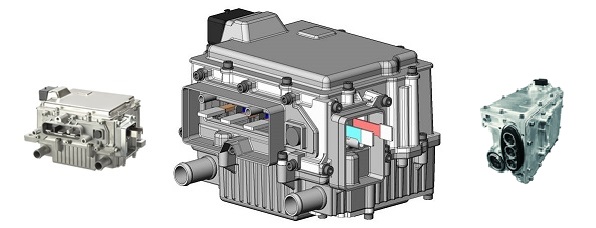
Hitachi Automotive Systems Americas, Inc. is in production on a "hybrid" vehicle. Hitachi Automotive Systems Americas, Inc.’s latest inverter that utilizes the technologies described above for higher density. Second-generation inverters used modules with single-sided direct cooling and were able to drive two motors.
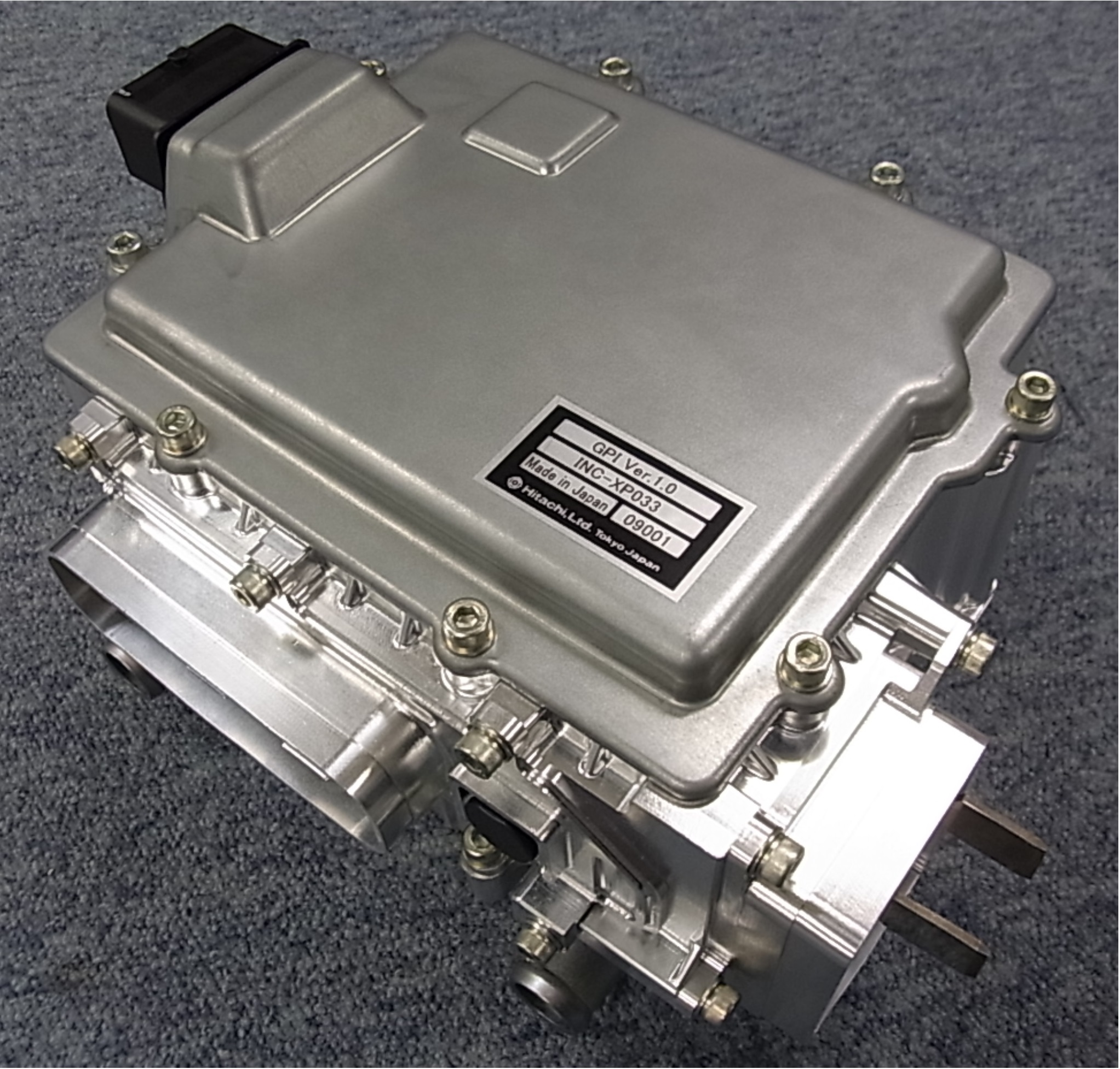 Third-generation inverter
Third-generation inverter
(1 motor)
Standard inverter
The third-generation models use modules
with double-sided direct cooling and feature a power
density of 35 kW/L, 5.6 times that of first-generation
models.
The thermal resistance of the power modules is improved at the expense of increasing the pressure loss in the cooling water channels. As this increases the resistance to water flow in the channels, the optimal point can be selected based on the cooling capacity. The power modules with double-sided direct cooling have approximately 35% better thermal resistance and providing a performance improvement of 30% or more in terms of current flow assuming use of power devices with the same chip size. Improvements in the performance of modules with double-sided direct cooling mean less rise in junction temperature, and because the inverter is able to operate with the cooling water at a higher temperature.